median nerve compression test at elbow|median nerve anatomy elbow : tv shopping Compressions of the median nerve at the elbow can occur both at the level of the fibrous laceration and the round pronator muscle. The former condition can cause painful . Nossos cursos são livres e gratuitos, oferecidos na modalida.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Encontra a galeria de fotos do filme Pânico (2022). 36 fotos .
what is median nerve entrapment
Pronator Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the median nerve at the level of the elbow. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain at the proximal volar forearm, sensory changes over the palmar cutaneous branch, . Pronator and anterior interosseous nerve syndromes are the two most common compression neuropathies of the median nerve occurring around the elbow. 22 Pronator syndrome occurs with.The median nerve can be entrapped at four locations around the elbow: distal humerus by the ligament of Struthers; proximal elbow by a thickened biceps aponeurosis; elbow joint between the superficial and deep heads of the .
If the patient starts feeling the typical CTS symp-tomatology (paresthesias over MN distribution in the afected hand), then the test is positive (abnormal). Another provocative test over the .
Compressions of the median nerve at the elbow can occur both at the level of the fibrous laceration and the round pronator muscle. The former condition can cause painful .
The median nerve compression test is also called Durkan’s test. Mostly commonly, compression of the median nerve results in carpal tunnel syndrome. Pathophysiology. Compression neuropathy arises when there is more than .FOREARM AND ELBOW Median Nerve. Proximal median nerve entrapment is rare. The primary clinical finding is pain in the proximal volar forearm. Other findings may include .How do you test for pronator syndrome? Pronator syndrome is typically diagnosed through a thorough physical examination. It is typified by tenderness over the elbow, and the median nerve, and on pronation the pain will increase .
Pronator syndrome (PS) is a compressive neuropathy of the median nerve in the proximal forearm, with symptoms that often overlap with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Because electrodiagnostic studies are often negative in PS, making .
At the elbow, the nerve passes to the inner side of the joint. Therefore, injuries in this area often cause median nerve pain. It also runs alongside the brachial artery. An acute injury to the median nerve here may . Furthermore, a positive median nerve compression test is positive when applying direct pressure over the transverse carpal ligament recreates symptoms of the carpal tunnel within 30 seconds. . Elbow Lesions. The median nerve can be involved during fractures-dislocations of the elbow, both directly by the fracture stumps that, in case of .
The median nerve can be entrapped at four locations around the elbow: distal humerus by the ligament of Struthers; proximal elbow by a thickened biceps aponeurosis; elbow joint between the superficial and deep .To diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome with high sensitivity and specificity, a positive median nerve compression test needs to be accompanied by a patient completed hand-diagram, the presence of night pain and abnormal sensibility by monofilament testing. . Culp R, Jacoby S. Musculoskeletal Examination of the Elbow, Wrist and Hand: Making the .The phalen’s test is a provocative test used in the diagnosis of CTS. This occurs when the median nerve is compressed or squeezed at the wrist. [4C,5F] The pain is often worst at night. Daily activities such as driving and typing may increase the symptoms. [5F] The most common complaints are; pain and tingling of hands and fingers Just distal to the elbow joint, the median nerve gives off its first terminal branch: the anterior interosseous nerve (AIN). . Phalen's test is used to assess for compression at the carpal tunnel. It is considered positive when there is a reproduction of symptoms after full flexion of the wrist for 60 seconds.
The research was done in 2016 to find a more suitable diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome among carpal compression test (CCT), Tinel’s test (TT), and Phalen’s test (PT). The study shows sensitivity and specificity of the Carpal compression test were higher than both Tinel's and Phalen's tests.If you have symptoms of nerve compression or damage, your healthcare provider may do a simple, noninvasive test to elicit Tinel’s sign. Tinel’s sign is a tingling feeling you get when your healthcare provider taps your skin over an affected nerve. Test results can help them diagnose nerve compression so you can get treatment to relieve .
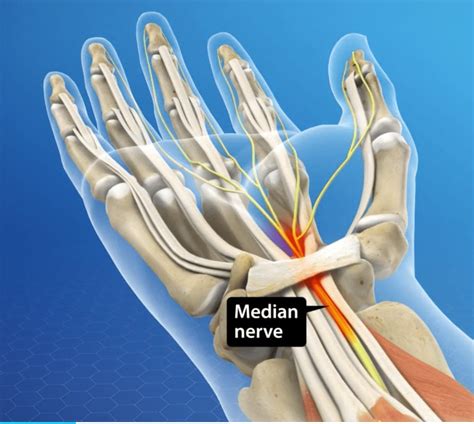
proximal median nerve compression
Evidence [edit | edit source]. Elbow flexion test as the sensitive of (0.32) provocative test in the diagnosis of cubital tunnel syndrome when combined with pressure on the ulnar nerve.. Research was done on 25 patients with cubital tunnel syndrome were tested preoperative and postoperative with 10 second elbow flexion test and 10 second shoulder internal rotation test. 80% of . Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when something puts pressure on your ulnar nerve in your elbow or wrist. Nerve entrapment is a type of nerve compression syndrome. . Flexing at the interphalangeal joint at the tip of the thumb may indicate a nerve problem. Tinel’s test: . There’s also a risk of surgical damage to your median nerve, ulnar .The median nerve is one of the main nerves in the hand. It originates as a group of nerve roots in the neck; these roots then come together to form a single nerve in the arm. The median nerve travels down the upper arm, across the elbow, and into the forearm, then passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist on its way to the hand and fingers.Median nerve entrapment at the elbow has also been reported secondary to an enlarged bicipitoradial bursa, prolonged external compression, and fracture or dislocation at the elbow 6. 9a. . In a complete AIN syndrome, as in the test case (Figures 1a and 1b),the flexor pollicis longus, radial half of the flexor digitorum profundus, and pronator .
Elbow Flexion Test; Tinel's Sign; Ulnar Nerve Compression Test; Lateral Epicondylalgia: Passive elbow extension, pronation, wrist flexion (Mill's Test) Resisted wrist extension with radial deviation (Cozen's Test) Resisted middle finger extension (Maudley's Test) Ligamentous Tests: Varus Stress Test; Valgus Stress Test; Moving Valgus Stress Test
Ulnar nerve entrapment: Compressed ulnar nerve in your elbow (cubital tunnel syndrome) or wrist (Guyon’s canal syndrome). Nerve compression syndromes that affect the lower limbs include: Meralgia paresthetica: Pressure on the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve in your thigh. Peroneal nerve compression: Pressure on the peroneal nerve in your .Figure 2: Median nerve entrapment at the pronator teres. The main symptoms of PTS include paresthesias in the dis-tribution of the MN, similar to CTS, but not preferent nocturnal . extends the patient’s elbow. The test is positive if the pain is re-produced. The patient´s elbow should be relaxed, otherwise, if .The test is positive if one or more of the following occurs: Symptoms reproduced; Side to side difference in elbow extension greater than 10 degrees; Contralateral cervical side bending increases symptoms, or ipsilateral side bending .Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow is called cubital tunnel syndrome. Numbness and tingling in the pinky and ring fingers are common symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome. . The test sends an electric current down the arm .
Pronator teres syndrome (PTS), first described by Henrik Seyffarth in 1951, is caused by a compression of the median nerve (MN) by the pronator teres (PT) muscle in the forearm. [1][2] The PT muscle is named because of its action and shape; it is a rounded muscle that pronates the forearm. In the majority of cases (66%), it arises from unequal two heads: the . Positive examination findings, including a positive pronator teres syndrome test, pronator compression test, and a positive Tinel sign over the median nerve at the antecubital fossa, also supported this working diagnosis. 14, 16 Intact function of the tested musculature helped to rule out other sites of nerve compression, because normal .
The hows and whys of median nerve compression in the forearm aren’t fully understood. For example, why do some people develop one type of neuropathy but not the other? . For example, a larger or wider bony bump along the inside of the elbow might be a factor. If the nerve passes close to this bump and gets trapped between the unusual shaped . Nerve compression syndromes of the hand present with various signs and symptoms that correspond to the nerve involved and its anatomic distribution. There are three nerves and their corresponding branches that provide sensory and motor innervation to the hand that include the median, ulnar, and radial. An understanding of the anatomy and distribution of . Phalen’s test is a series of movements and positions that help your healthcare provider diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome. You’ll move your hands and wrists into a position that puts light pressure on the median nerve in your wrist. If you feel tingling or numbness in your hands or fingers, you probably have carpal tunnel syndrome.
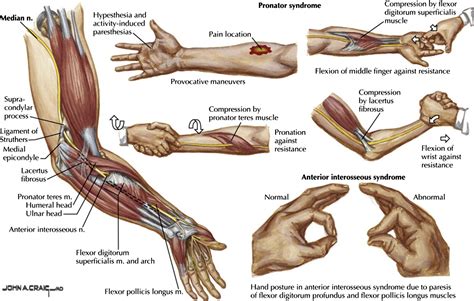
Anatomical Course. The median nerve is derived from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus.It contains fibres from roots C6-T1 and can contain fibres from C5 in some individuals. After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla, the median nerve descends down the arm, initially lateral to the brachial artery.Halfway down the arm, the nerve .
Positive examination findings, including a positive pronator teres syndrome test, pronator compression test, and a positive Tinel sign over the median nerve at the antecubital fossa, also supported this working diagnosis. 14, 16 Intact function of the tested musculature helped to rule out other sites of nerve compression, because normal .
Nerves are bundles of string-like fibers that send and receive messages between your brain and your body via electrical and chemical changes in the cells. There are three main nerves in your arm: the median, the ulnar and the radial.The ulnar goes from your neck down your arm and to your hand. You may have cubital tunnel syndrome if your ulnar nerve is .The median nerve passes through the cubital fossa and passes between the two heads of pronator teres muscle into the forearm. It then runs between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus muscles and enters the hand through the carpal tunnel. [10]It innervates most of the flexor muscles in the forearm and hand. Its sensory component .Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is the most common nerve entrapment syndrome, affecting approximately 3.8% of the general population [1]. The pathophysiology involves increased pressure on the median nerve as it traverses through the carpal tunnel leading to impaired blood flow, inflammation, and ischemic injury of the nerve [2].
12 de abr. de 2022 · Musa do OnlyFans sobre família naturista: 'Pessoas acham isso surreal'. Natasha Steffens atraiu os holofotes depois de revelar que gravava seus .
median nerve compression test at elbow|median nerve anatomy elbow